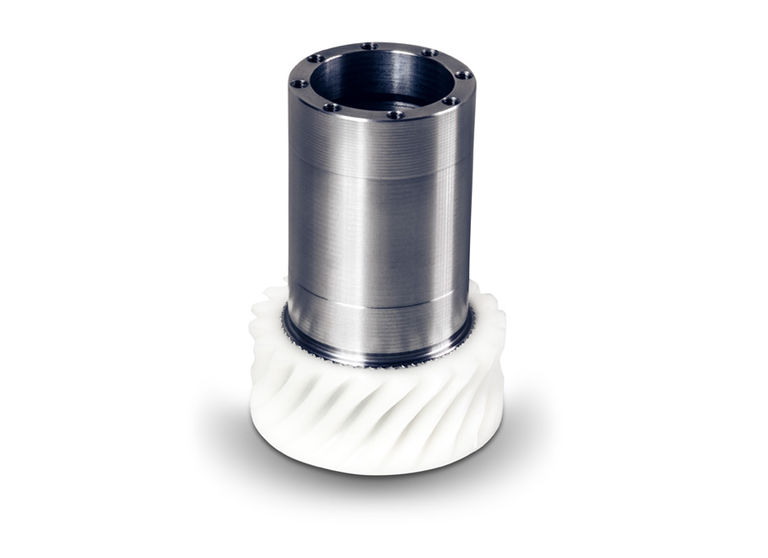
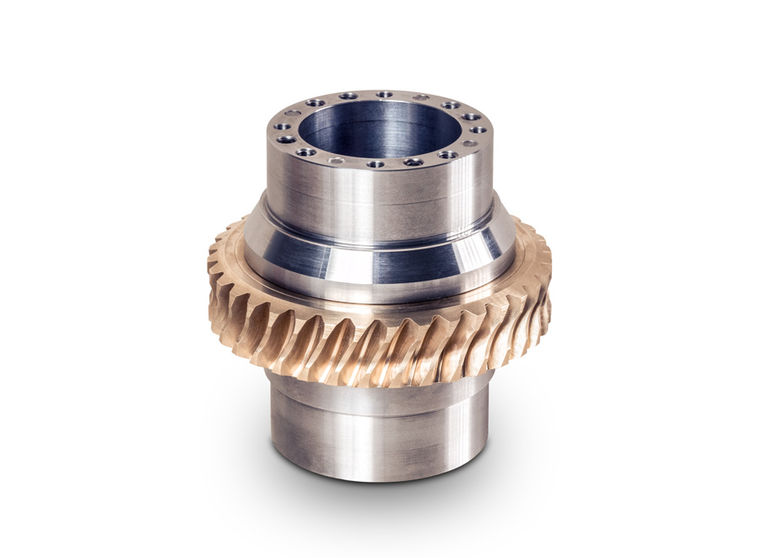
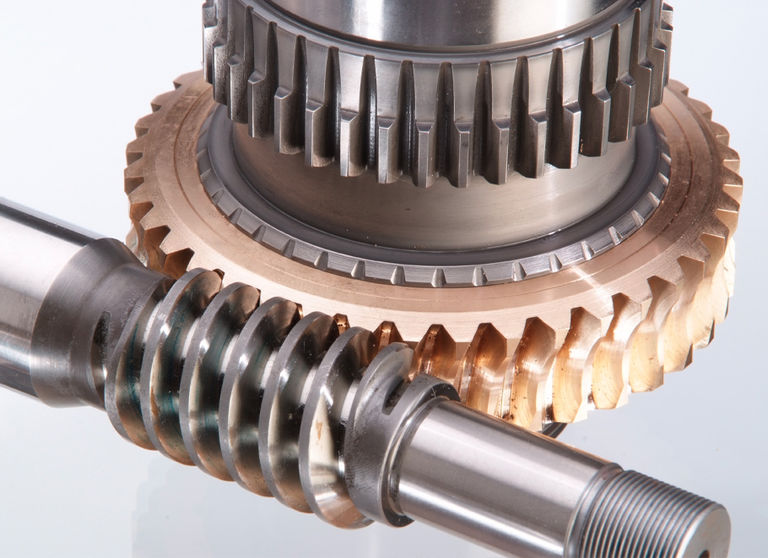
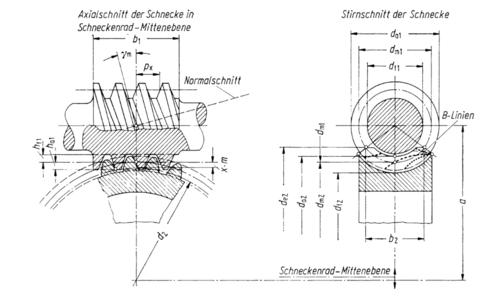
A worm gear set, also known as a worm gear transmission, is a special form of transmission that comprises a worm shaft and a worm gear.
- First of all, the tooth form is specified with the module (m), which indicates the distance between the teeth (pitch px).
- Together with the diameter of the worm shaft, this module determines the center pitch angle (γm) of the worm.
- Furthermore, the pressure angle (α) between the worm and the gear is defined, which indicates the inclination of the worm flank.
- Another important parameter is the number of teeth (z) of the worm gear.
- This is also responsible for the number of teeth on the gear wheel.
- The pitch (p) of the worm indicates how far the worm moves forward axially per revolution.
- The profile displacement (x) describes the displacement of the worm wheel profile along the worm wheel axis.
- Finally, the transmission ratio (i) indicates the relationship between the speed of the worm and the worm wheel, which determines the basic function of the worm wheel gearbox.